Description
Base oil is a type of oil that is used as a raw material in the manufacture of various lubricants and greases. It is a refined petroleum product that is produced through a process of distillation and refining. Base oils are classified based on their properties, such as viscosity, volatility, and sulfur content, among others. These properties determine the quality and performance of the lubricants and greases that are made from them.
There are different types of base oils, including mineral oils, synthetic oils, and vegetable oils. Mineral oils are the most common type of base oil and are produced from crude oil through a process of distillation and refining. Synthetic oils, on the other hand, are made from chemically engineered compounds and offer superior performance compared to mineral oils. Vegetable oils are made from plant-based sources, such as soybeans, canola, or palm, and are often used in environmentally friendly lubricants.
Base oils are used in the manufacture of a wide range of lubricants and greases, including engine oils, industrial oils, hydraulic oils, gear oils, and transmission fluids, among others. Lubricants and greases are used to reduce friction and wear between moving parts, protect against corrosion and oxidation, and cool and clean the equipment.
The performance of lubricants and greases depends on the quality and properties of the base oil. For example, a high-quality base oil with a high viscosity index will provide better performance at both high and low temperatures. High-quality base oils also have lower levels of impurities, such as sulfur and nitrogen, which can cause corrosion and wear in the equipment.
Base oils are available in different grades, which are based on their properties and intended use. The American Petroleum Institute (API) has developed a classification system for base oils, which includes five groups based on their level of refining and performance characteristics. Group I base oils are the least refined and have the lowest performance, while Group V base oils are the most advanced and offer the highest performance.
In summary, base oil is a critical raw material in the manufacture of lubricants and greases. Its properties determine the performance and quality of the finished product, making it essential to select the right base oil for the intended application. With ongoing research focused on developing new and innovative base oils, lubricants and greases are expected to continue to evolve and improve in the years to come.
Usages
Base oil is a crucial component in the manufacture of various lubricants and greases that are used in a wide range of applications, including:
- Automotive: Base oils are used in the manufacture of engine oils, transmission fluids, and other automotive lubricants. These lubricants help to reduce friction and wear between moving parts, protect against corrosion and oxidation, and cool and clean the engine.
- Industrial: Base oils are used in the manufacture of industrial lubricants that are used in a variety of applications, including hydraulic systems, gearboxes, compressors, and turbines. These lubricants help to extend the life of the equipment, reduce maintenance costs, and improve overall equipment performance.
- Marine: Base oils are used in the manufacture of marine lubricants that are used in engines, gears, and other equipment on ships and other marine vessels. These lubricants help to protect against corrosion and wear in the harsh marine environment.
- Aviation: Base oils are used in the manufacture of aviation lubricants that are used in aircraft engines, landing gear, and other critical components. These lubricants help to ensure safe and reliable operation of the aircraft.
- Metalworking: Base oils are used in the manufacture of metalworking fluids that are used in cutting, drilling, and other metalworking processes. These fluids help to reduce friction and heat, improve surface finish, and extend the life of the cutting tools.
- Food grade: Base oils are used in the manufacture of food-grade lubricants that are used in the food and beverage industry. These lubricants are specially formulated to meet strict safety and regulatory requirements and are used to lubricate equipment in food processing and packaging.
- Textile: Base oils are used in the manufacture of lubricants that are used in the textile industry. These lubricants are used to reduce friction between fibers and improve the quality and performance of the finished textile products.
Overall, base oils are used in a wide range of applications and industries, and their performance plays a crucial role in the performance and reliability of the equipment. Ongoing research and development are focused on improving the quality and performance of base oils to meet the evolving needs of different industries and applications.
Recycled base oil, also known as re-refined base oil, is a type of base oil that is produced from used lubricating oil that has been collected and reprocessed. Base oil is a key component in the formulation of lubricants, which are used to reduce friction and wear between moving parts in machinery and equipment.
Recycling base oil offers several benefits, including:
- Environmental benefits: Recycling base oil helps to reduce the amount of used oil that is improperly disposed of, which can have a negative impact on the environment. Used oil can contaminate soil and water, and can also release toxic chemicals into the air if it is burned.
- Energy savings: Recycling base oil requires less energy than producing new base oil from crude oil. This is because the used oil has already been refined once, so it requires less processing to be turned into usable base oil again.
- Cost savings: Recycling base oil is often cheaper than producing new base oil from crude oil. This is because the used oil is typically less expensive than crude oil, and the refining process is less energy-intensive.
The process of recycling base oil involves several steps, including:
- Collection: Used oil is collected from various sources, such as auto repair shops, oil change facilities, and industrial sites.
- Pre-treatment: The used oil is pre-treated to remove any contaminants, such as water, dirt, and metal particles. This is typically done through a filtering process.
- Re-refining: The pre-treated oil is then re-refined using a process similar to the refining of crude oil. This involves distillation, cracking, and hydrotreating to remove impurities and restore the lubricating properties of the oil.
- Blending: The re-refined base oil is then blended with additives to improve its performance and meet the specific requirements of different applications.
Recycled base oil is a viable alternative to virgin base oil, and it offers several benefits in terms of environmental sustainability, energy savings, and cost savings. However, it is important to ensure that the recycled base oil is properly processed and meets the necessary quality standards to ensure its safety and effectiveness.
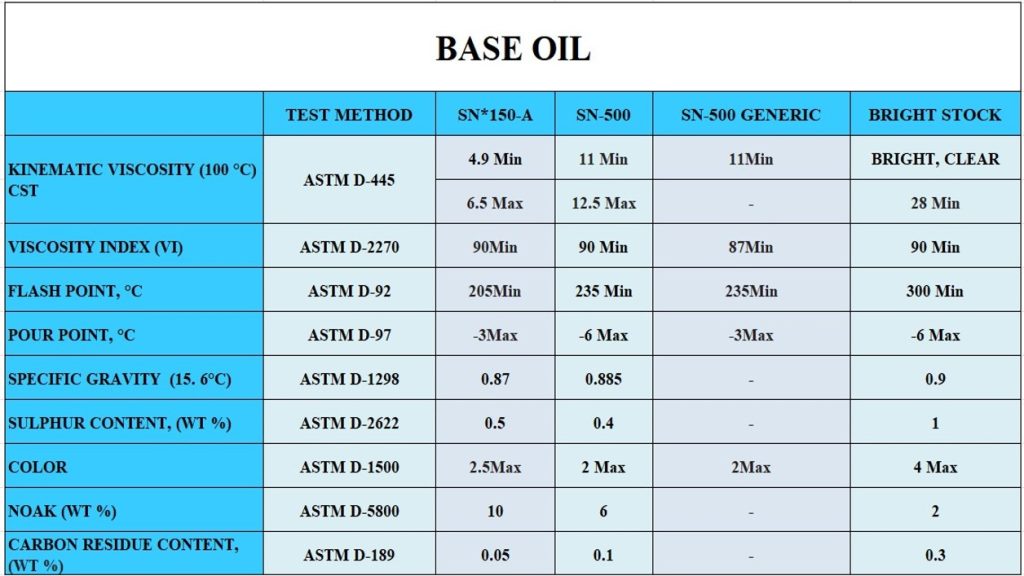
Specification